Real-Time Bidding is a revolutionary digital advertising method that has simplified the ad space-selling process for the publishers. But, what is RTB in marketing? And what importance does it hold in the ad-buying process? We will cover everything about Real Time Bidding (RTB) in this blog.
Real time bidding, since its advent in 2014, has transformed the way advertising functions. It is RTB that gave way to programmatic advertising. Many experts from around the globe have weighed in on the importance of RTB in marketing, and how it has addressed the gaps that traditional advertising couldn’t.
In this blog, we will explore what RTB is and how it has been shaping the programmatic advertising industry.
What is Real-time Bidding? (RTB Meaning)
Real-time Bidding (RTB) is a form of programmatic buying that allows advertisers to bid to display ads to internet users in real-time, without manual interventions. The meaning of RTB is in its name – ad space transactions happening in real-time (when the user is on the website).In fact, the RTB market is experiencing significant growth due to the increased adoption of full cycle software development, website design, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML).
If you are asking why, the concise answer is that the RTB algorithm allows increased control to the publishers in managing their advertisement inventory.
In simple words, the real time bidding algorithm is a software that facilitates the transaction of ad space in real-time. All the RTB processes, from bidding to ad placement, take place when the user is on the website within 100 milliseconds.
Now that we have covered the real time bidding definition, let’s look at its subsets.
Subsets of Real-time Bidding
There are two subsets of real time bidding that blend direct and programmatic advertising to maximize ad revenue. Here they are:
1. Mobile Real-Time Bidding
As the name suggests, Mobile RTB sells mobile ad inventory in real-time. However, it has challenges like general targeting as cookies can’t be tracked in mobile RTB or variations in protocols in web-based and app-based inventory (the two having separate advertising protocols). The two follow a different set of protocols to run an RTB auction. Nonetheless, due to a rise in mobile users, the mobile advertising market is flourishing.

2. Video Real-Time Bidding
OpenRTB, proposed by IAB, now supports the VAST (video ad serving template) type of placement for showing video ads as soon as a user (impression) appears on the site. Video marketing is an impactful medium, with 90% of users saying they find video ads helpful in making decisions.
Premium publishers (like Forbes) are already implementing video RTB to maximize their inventory profits.
What are the Components of Real-time Bidding?
There are three components of real-time bidding.
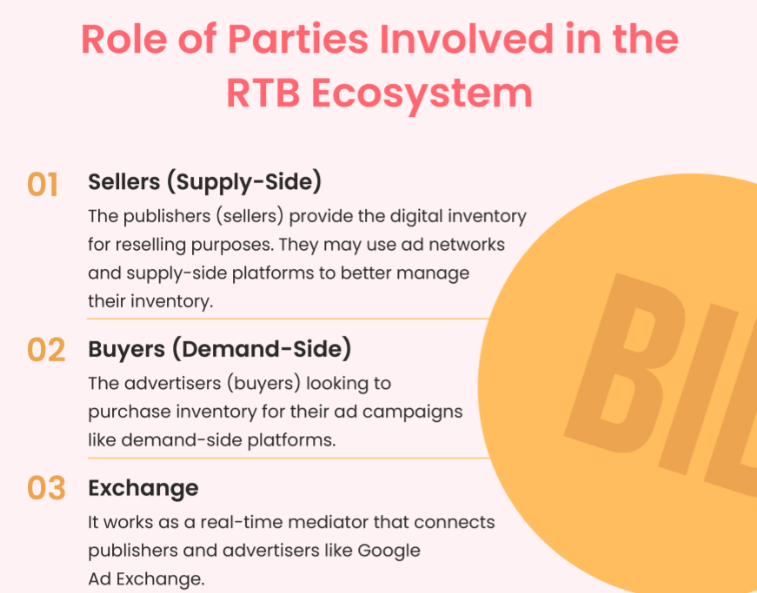
1. Supply-side Platform
SSP is a software publishers use to manage and sell their ad inventory. The supply-side platform integrates with various ad exchanges and ad networks, makes the ad space available to the advertisers, and selects the winning bid for displaying the ad.
2. Demand-side Platform
What is SSP to a publisher is DSP to an advertiser. It’s a technology used by advertisers to manage their ad campaigns. Demand-side platform offers many benefits to the advertiser, such as selecting the best ad space, providing detailed insights into the ad campaigns in real-time, optimizing budget spending, and avoiding fraudulent ad inventories.
3. Ad Exchange
The next component in real-time bidding is an ad exchange. It is a marketplace that brings publishers and advertisers together on the same platform to exchange impressions. Compared to ad networks, ad exchanges provide more transparency and a wider audience of advertisers for the ad space.
How Does RTB Work? (Real-time Bidding Process)
Real-time bidding auctions are very similar to that of the stock market. Let’s understand how. When a share becomes available in the stock market, buyers compete for it, and the highest bidder gets the share.
Likewise, advertisers must bid on available impressions in an online media exchange to put their ads on the publisher’s website. The highest bidder gets the ad space, and the process renews for the next impression.
The analogy must have given you an idea of the RTB process. Let’s understand the real time bidding process step-by-step.
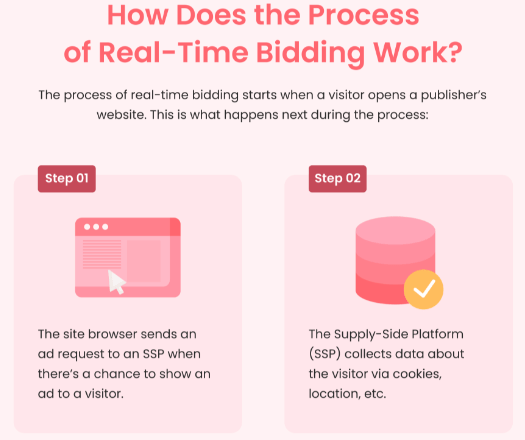
Once the site browser identifies a potential ad placement opportunity, it triggers the next step, where the Supply-Side Platform (SSP) starts gathering data about the visitor.
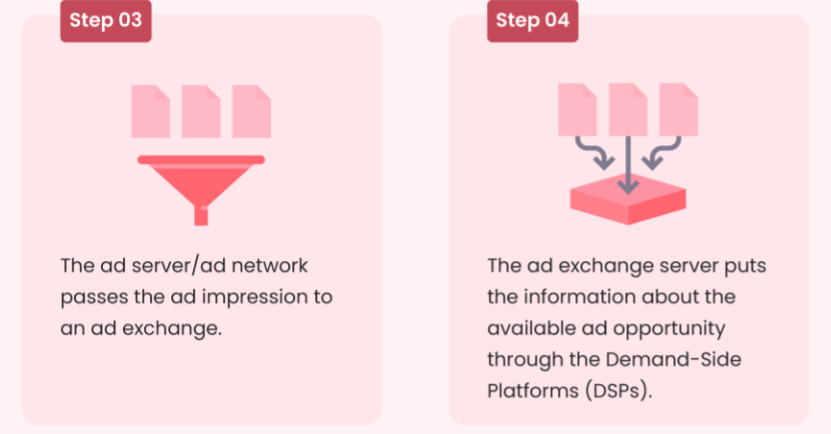
As shown in the image above, with the collected visitor data in hand, the SSP sends the request to the ad server, which is responsible for delivering the ad to the ad exchange.

As the DSPs receive the details of the ad opportunity, they begin analyzing the data and submit their bids based on the target audience, budget, and relevance
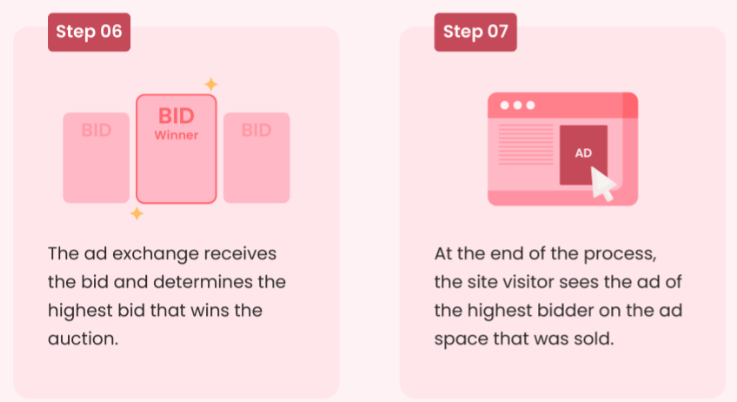
Among the submitted bids, the ad exchange selects the highest bidder, ensuring the most relevant ad is chosen for the visitor. And finally, the highest bidder’s ad is displayed to the site visitor, completing the automated auction process.
2 Real-World Examples of Real-Time Bidding
“Real-time bidding” derives its name from the impression prices being set in real-time based on what buyers are ready to pay. For example, suppose the user data states that the visitor is a recurring user and has previously engaged with Amazon ads. In that case, Amazon will bid higher on the impression than other advertisers as the chances of conversion will be higher.
Here’s another example of RTB in advertising. Consider a user who spends much time on fashion websites, checking the newest collections and shopping for apparel. While surfing, the user arrives at a website that uses RTB ads.
Meanwhile, a fashion company and a luxury cosmetics company have both signaled interest in users with similar interests. The RTB system recognizes the compatibility between the users’ interests and the advertisers’ requests, and they bid on the impression. The advertiser that places the highest bid wins and gets to display the ad to the website visitor.
The entire RTB process takes a split second. The advertiser usually sets up their ad campaign prior while the system handles their bids and sends timely bid responses.
Why is Real Time Bidding Important for Publishers & Advertisers?
Real time bidding has changed the way advertising is done. What used to take rounds of negotiations can now be done within a fraction of a second. The RTB algorithm offers numerous advantages to both publishers and advertisers alike. For publishers, it has broadened the reach of their ad inventory. Also, publishers can earn more by cashing on the quarterly fluctuations in the bids, and sell premium placements via private auctions.
For advertisers, RTB has brought more ad space into the programmatic ecosystem. With the availability of user information (demographics, geolocation, behavioral data etc), advertisers can now display ads based on the user’s interest rather than using just the websites as their proxy.
What are the Types of Real-Time Bidding?
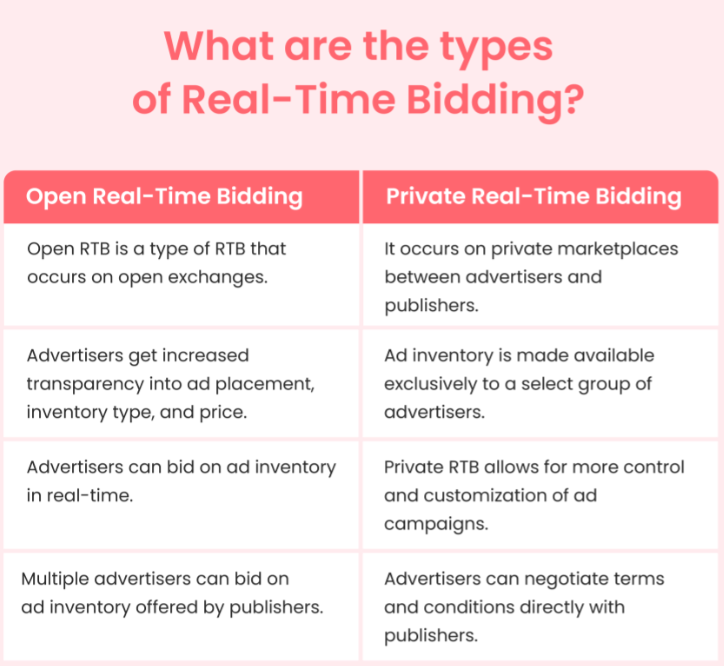
There are two main types of real-time bidding (RTB): open RTB and private RTB.
1. Open Real-Time Bidding
Open RTB is a type of real-time bidding that occurs on open exchanges, where multiple advertisers can bid on ad inventory made available by publishers.
Advertisers can bid on ad inventory in real-time in open RTB auctions using software that automates the process.
2. Private Real-Time Bidding
Private real-time bidding, or programmatic direct, is a type of RTB that occurs on private marketplaces or through direct deals between advertisers and publishers.
In private real-time bidding, ad inventory is made available exclusively to a select group of advertisers rather than being open to all advertisers on an exchange.
Private RTB allows for more control and customization of ad campaigns, as advertisers can negotiate terms and conditions directly with publishers.
How Much Does Real-time Bidding Cost?
The real-time bidding cost is calculated through CPM or cost per mille. It means the amount paid by the advertiser for every thousand impressions. On the publisher’s side, RTB cost is calculated through eCPM or effective cost per mille. Subtracting the percentage (say 15%) of the ad exchange charges as its commission from the CPM gives you eCPM. CPM depends on how effective the ad campaign is.
Simply put, CPM is inversely proportional to the ad campaign’s effectiveness. The higher the CPM, the lower the effectiveness of the campaign.
The dynamicity of programmatic advertising provides flexibility to the advertisers and the publishers. Unlike traditional advertising, where the costs and the ad creatives are fixed, the advertiser can easily optimize their campaign in real time through programmatic advertising.
Similarly, real-time bidding also allows advertisers to adjust bid prices to make their campaigns more lucrative. The publishers can tweak their floor prices depending on the inventory’s demand.
What Are the Advantages of Real-Time Bidding?


Improved inventory pricing
RTB allows publishers to set a floor price for their inventory. This enables them to optimize their inventory as publishers can extract the exact value of their inventory in real time.

Handling remnant ad units
Real-time bidding helps publishers get a fair price for remnant ad units by making them available at various auctions.

Ad unit modifications
Publishers can modify their ad units individually at any point in time via ad testing to optimize their inventory. They can change the floor price, ad placements, and targeting options anytime at the ad unit level.

Transparency
Both publishers and advertisers can monitor their most-viewed and low-performing ad units and set their floor prices accordingly.
Save Money
Advertisers can save money on second-price auctions and pay just $0.1 more than the second bid.
What are the Challenges With Real-Time Bidding?
Even with all the benefits offered by real-time bidding, some challenges still make RTB programmatic buying not as effective as it was designed to be. Here are some of those:
- Data leakage: Laws like the CCPA, GDPR, and others prioritize user protection in some areas, which makes it challenging for publishers to determine whether to share user data for targeting. It gets further complicated with varying rules governing the storage and use of data.
- No guaranteed deal: RTB depends on the demand-and-supply rule, unlike programmatic guaranteed deals. This can jeopardize the publisher’s earnings as low demand will mean lower or lesser bids, leading to low ad earnings.
- Brand safety: While advertisers need optimal placement for their advertising, publishers seek control over the ads that appear on their websites to maintain quality and safety. Third-party platforms like Trust Metrics can address these concerns by allowing publishers to create blocklists for certain types of content and ads.
What is the Difference Between Real-time Bidding and Programmatic Advertising?
| Feature | Real-Time Bidding (RTB) | Programmatic Advertising |
| Definition | A type of deal under programmatic advertising that holds real-time auction for ad impressions | An umbrella term that automatizes buying and selling of ad space |
| Types | Includes header bidding, first-price auction, second-price auction | Includes Private Marketplace, Preferred Deals, Programmatic Direct |
| Process | Bidding happens in real-time; bids and floor price can be adjusted in real-time based on demand and data | Uses algorithms to handle ad space transactions but not always via auctions (programmatic guaranteed) |
| Ad Inventory | Bought on per impression basis | Acquires ad space either on per impression basis or in bulk (programmatic deal) |
| Targeting | Nuanced targeting by using real-time insights | Refined targeting based on user segmentation data |
| Cost | Set by the bidding process where the winning bid gets to display their ad | Determined by automated methods or fixed prices in case of programmatic guaranteed |
| Efficiency | Optimizes targeting and ad spend | Streamlines ad buying/selling as ad inventory can be bought from a single source (DSP) |
| Usage | Best suited for scenarios requiring real-time decision-making. | Versatile, covering various automated buying strategies. |
What is the Difference Between Real Time Bidding and Header Bidding?
Header bidding is a type of real-time bidding, rather a more advanced version. In header bidding, the auction takes place in a simultaneous fashion. Although this sounds a lot like RTB, there are a few minor variations. Header bidding enables all ad exchanges to bid on several auctions at once via RTB, in contrast to traditional real-time bidding, which involves each ad exchange conducting its own auction one at a time.
Let’s explore this approach in a more detailed manner:
In traditional real-time bidding, bid ads are served one by one based on the floor price set by publishers. The moment the floor price is met, the auction ends, even if other advertisers in the sequence have a lot more to offer than the set floor price.
Why are Bids Higher Than the Floor Price not Considered in Traditional Real-time Bidding?
It’s simply because the floor price is met. The traditional method does not further analyze the bids since it consumes more time. The priority here is to meet the floor price and deliver ads to the publishers’ website in a timely manner.
Think of it as going from one shop to another, won’t it be time-consuming and delay the ad delivery to the website?
Thus, it resorts to the floor price and no longer looks for higher bid opportunities.
In header bidding, the moment a highest bid is found, even if it exceeds the floor price, the auction ends. Header bidding has everything traditional real-time bidding lacks. It does not need to go from one shop to another in search of the highest bid. This centralized approach of header bidding ensures that publishers receive the highest bid.
Top Real-time bidding platforms 2025
There are many popular RTB platforms that you can leverage to double-down your profits, like:
- Outbrain
- OpenX
- Imonomy
- Microsoft Advertising (Formerly Xandr)
- LiveIntent
- Smaato
- Magnite
How to Make the Most Out of Real Time Bidding?
For RTB to be able to expand, there are a few elements that both publishers and advertisers need to take into consideration:
- Partnering with the right header bidding solution to secure user data and witness significant growth in RTB.
- Monitoring the user data flow and allowing transparency in data sharing to avoid data fraud.
- Complying with ad safety measures by applying ad fraud prevention techniques to prevent ad fraud.
- Identifying premium sections of ad inventory and minting profits via private auctions.
- Opting for page load optimization techniques like lazy-loading to serve ads faster while maintaining the user experience on your website.
The Future of Real-Time Bidding (RTB) in 2025 & Beyond

Despite its advantages and disadvantages, real-time bidding is so huge that programmatic buying and RTB are often used as synonyms, which is incorrect. RTB is a type of programmatic buying.
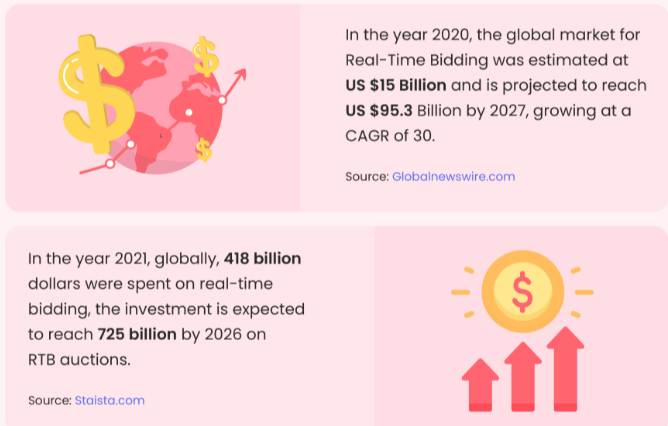
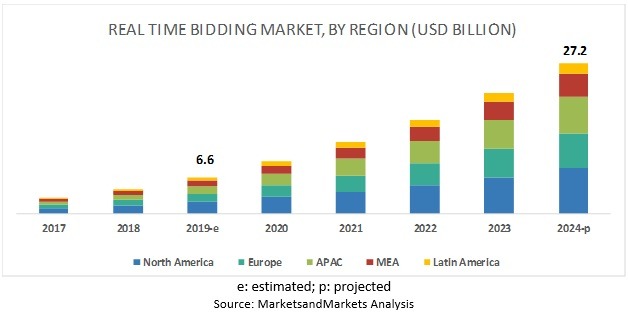
Moreover, current statistics show that RTB would have captured 32.9% of the ad tech by 2024. RTB spending will grow from USD 6.6 billion to USD 27 billion. Market penetration and data intensity have to be the two major reasons that helped RTB to become this successful.
Here’s how:
Market penetration refers to the fact that publishers and marketers are using real-time bidding. Growth is fueled by RTB capturing the market share for indirect sales. The second driver behind the growth in RTB spending is the data intensity of the campaign, which was generated by the enhancement in the quality and the use of data.
The newly developed algorithms use the data as a key input in determining the real value of the impressions, improving the key performance indicators.
Real-Time Bidding optimization is necessary for increasing the ROI from your ad campaigns and empowering your brand to grow better. Sign up for expert advice at AdPushup today!

Frequently Asked Questions
Real-time bidding (RTB) is a digital advertising process in which advertisers bid on the opportunity to display ads to internet users in real time. An auction gets triggered when a user visits an RTB-enabled website or app. The advertisers bid on the impression, and the highest bidder displays their ad to the user.
Real-time bidding has many benefits, such as showing ads based on user rather than available ad space, delivering highly targeted and personalized advertising to internet users, and optimizing ad campaigns to save time and money.
Real-time bidding (RTB) allows publishers and advertisers to target users based on campaign insights and user data (demographic data, behavioral data, contextual data, etc.) to reach their desired audience with high precision.
The auctions done by RTB take between 30-100 milliseconds to complete and serve ads to the users.
Yes, Google AdX (Google’s ad exchange) uses real time bidding similar to other ad exchanges.
Programmatic advertising is a form of advertising that involves real-time bidding, wherein the RTB algorithm facilitates the ad space transactions between the publishers and advertisers in real-time.
PPC or Pay-per-click advertising is the form of advertising that involves bidding. On the other hand, for real-time bidding, it is programmatic advertising. To be specific, RTB is an integral component of advertising that facilitates the buying and selling of ad space in real-time.