Choosing one between header bidding and ad mediation can be a tricky choice as one needs to be well-versed with the nuts and bolts of both these technologies. That’s why we’ve come up with this blog. So dive in and discover valuable insights about header bidding vs ad mediation.
Have you ever heard of the idiomatic expression “bidding war”? Well, if you’re one of the players in the ad tech industry, you’ve probably heard of it and even experienced it firsthand. That’s because when it comes to monetizing digital content, the competition can be fierce.
Why? Let’s face it: publishers and advertisers strive to increase their revenue and put in their best efforts to attain those goals. If you’re one of them, you must have come across terms – header bidding vs ad mediation.
What is Header Bidding & Ad Mediation?
Header bidding vs. ad mediation – two popular techniques publishers use to optimize ad revenue. Both options have evolved, with new capabilities and features constantly being added.
In fact, Taboola recently expanded its native bidding service with the launch of Taboola Header Bidding, enabling advertisers to reach new suppliers and helping publishers generate incremental revenue from their display ads inventory.
Ad mediation has also kept pace with advancements in the ad tech industry. For example, ironSource, a leading mobile monetization platform, offers a hybrid mediation solution that enables mobile app developers to access multiple demand sources and optimize their ad inventory.
In this blog post, we’ll break down the basics of header bidding vs ad mediation and understand their difference, pros, and cons. So, sit tight and get ready to bid for the best ad revenue.
But before we delve deep into the topic, let’s glance at the differences.
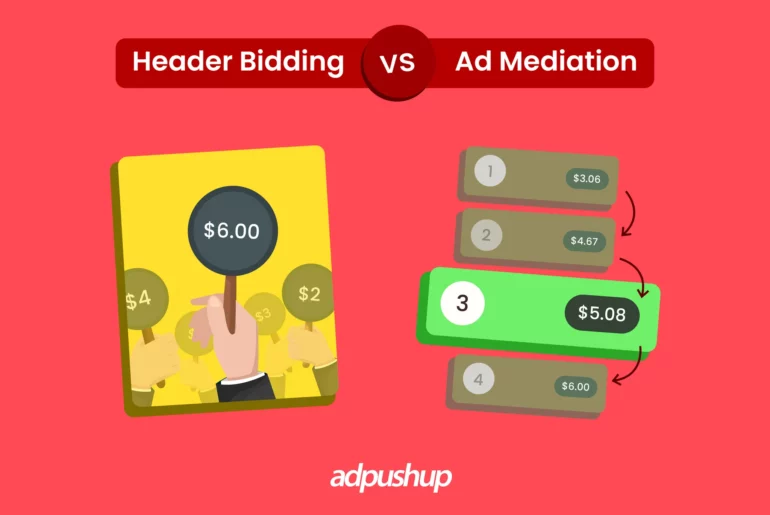
Header Bidding vs Ad Mediation
| Header Bidding | Ad Mediation |
| Publishers offer ad inventory to multiple ad exchanges simultaneously | Multiple ad networks are integrated into a single ad server |
| Bidders compete in real-time for ad inventory | Ad server selects the best-performing network based on predefined rules |
| Can result in higher revenue for publishers as inventory is sold to the highest bidder | Helps publishers optimize ad inventory by selecting the best network for each impression |
| Implementation requires inserting a header tag on website’s header | Implementation requires integrating multiple ad networks into a single ad server |
| More complex implementation but can result in higher revenue potential | Easier implementation but may not result in maximum revenue potential |
| Reduces page latency as impressions are offered simultaneously to the ad networks | Increases page latency as impressions are offered one-by-one to the ad networks |
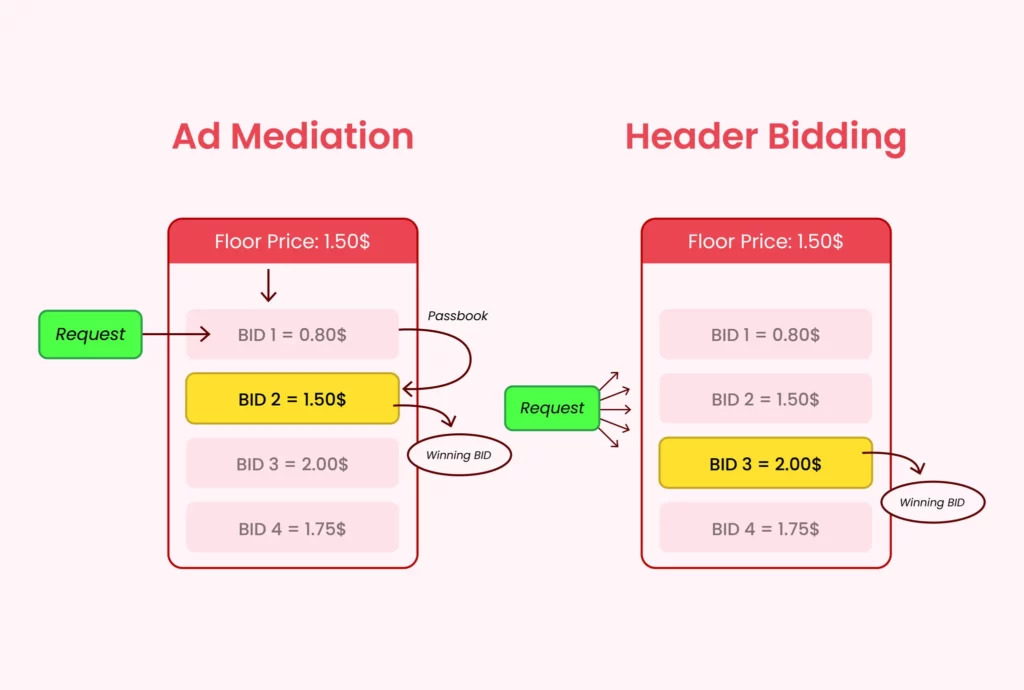
Now that we have looked into the differences, let’s first get to know what header bidding is and how it benefits the publishers.
What is Header Bidding?
As a quick refresher, we’ve covered header bidding and its aspects in previous blog posts. But for those unfamiliar with the term, let’s quickly define it briefly. Ideated back in 2014 and made its way into the mainstream in 2016, header bidding is a technique publishers use. It allows them to offer their ad inventory to multiple SSPs (Supply Side Platforms) and ad exchanges before requesting the ad servers.

How Does Header Bidding Work?
Header bidding starts with embedding JavaScript code in the webpage’s header section. When a user visits the site, this code triggers and sends bid requests to various ad networks, SSPs, and ad exchanges all at once.
These demand partners then conduct quick internal auctions, determining their highest bid for the impression. The top bids are collected within the user’s browser and sent to the publisher’s ad server before calling any direct inventory.
Note: Only if there is no suitable bid from the header bidding process does the ad server then consider direct inventory or other ad sources.
This simultaneous auctioning enables publishers to see the highest bids upfront, ensuring they get the best possible price for their ad space.
Through this process, publishers can control which sources participate, leading to increased competition and higher ad prices. This method also reduces reliance on a single SSP (Supply Side Platforms), increasing the ad fill rate and optimizing yield.
Moreover, since the auction happens in a single event rather than sequentially, reporting discrepancies are minimized, which provides more accurate and streamlined results. Ultimately, header bidding ensures better exposure for advertisers and maximizes earnings for publishers.
How does Header Bidding benefit Publishers?
Header bidding offers several benefits to publishers, such as:
Increases Competition among Bidders
Unlike the waterfall method, header bidding increases the bid pressure by letting the advertisers bid simultaneously. This drives competition for the particular impression, increasing the eCPM for the publishers.
Higher eCPMs and Fill rates
Header bidding exposes the publisher to a wide pool of advertisers, which in turn, increases the opportunity for publishers to fill their ad inventory at a faster rate. This enables publishers to demand higher eCPMs for their ad space.
Reduced Latency
Server-side header bidding reduces latency compared to client-side methods by conducting the bidding process on the server. This ensures faster page load times and a better user experience while maintaining competitive bidding dynamics.
Better Control and Transparency
Header bidding also gives you more control and transparency over your ad monetization. You can see the bids and performance of each demand source, making it easier to decide which ads to display and which to pass on.
Another benefit of header bidding is that it allows you to diversify your demand sources. This reduces your dependency on any single network, which can be a game-changer if one of your networks experiences a dip in performance or goes offline.
Challenges and Limitations of Header Bidding
Header bidding has surely transformed the landscape of online advertising, but it is not without its challenges and limitations. Here are a few of them:
It Slows Down the Loading Speed
As header bidding allows you to work with multiple demand partners simultaneously, it slows down the loading speed of the web page. As a result, it negatively affects the user experience. To fix this, you can go for server-side header bidding.
Reduced Transparency With Third-party Prebid Servers
When you are using a third-party prebid server, which also works as a demand source, you can’t expect any transparency. Such servers often prioritize their own bids, which will leave you wondering why they are winning.
Requires Technical Expertise
One of the challenges you may have when dealing with header bidding is that it requires technical expertise. You’ll have to choose and configure the header bidding wrapper, manage the ad units, transform the list of demand partners, and handle other tasks like these that require technical expertise. If you’re not a tech-savvy person, hiring a professional for the same tasks can be a wise initiative.
Duplicate Bids
Most advertisers often use multiple DSPs to maximize their reach and publishers may work with numerous SSPs. This results in redundancy in the bids, and similar bids end up competing against each other. This leads to inefficiencies and potential revenue loss.
That said, let’s now understand what ad mediation is.
What’s Ad Mediation (Waterfall Method)?
Ad mediation, on the other hand, refers to the technology that enables publishers to manage multiple demand sources and ad networks within a single platform. What’s different about it? It gives you more control, such as the ability to set up rules and preferences for each ad network. These rules and preferences can include priority, fill rate, and eCPM.
Based on your preferences, the ad mediation platform will look for the best ad network to serve the ads. It helps publishers save considerable time as they won’t have to manually optimize their fill rate and revenue across different ad networks.
Though both have some similarities, they differ in multiple ways. That said, let’s now take a look at the differences they share.
Let’s have a look at the formula using which publishers are increasing their ad revenue through the ad mediation platforms.
Ad revenue = Ad request* Fill rate* eCPM
How does Ad Mediation Work?
When a user navigates to the website, an ad request is sent to the mediation platform, including details such as user demographics, site data, and ad placement information. The mediation platform then communicates with multiple ad networks, which invites them to bid on the ad impression.
These ad networks evaluate the request based on their targeting criteria and bid the amount they are willing to pay for the impression. The ad mediation platform selects the highest bid from the participating ad networks, sometimes using a waterfall model where networks are ranked, and the highest-ranked network with available ads fills the request.
The mediation platform also tracks the performance of each ad network, such as fill rates, CPMs, and user engagement, using this data to optimize future ad requests. It opens the door for publishers to gain more revenue by integrating with multiple ad networks.
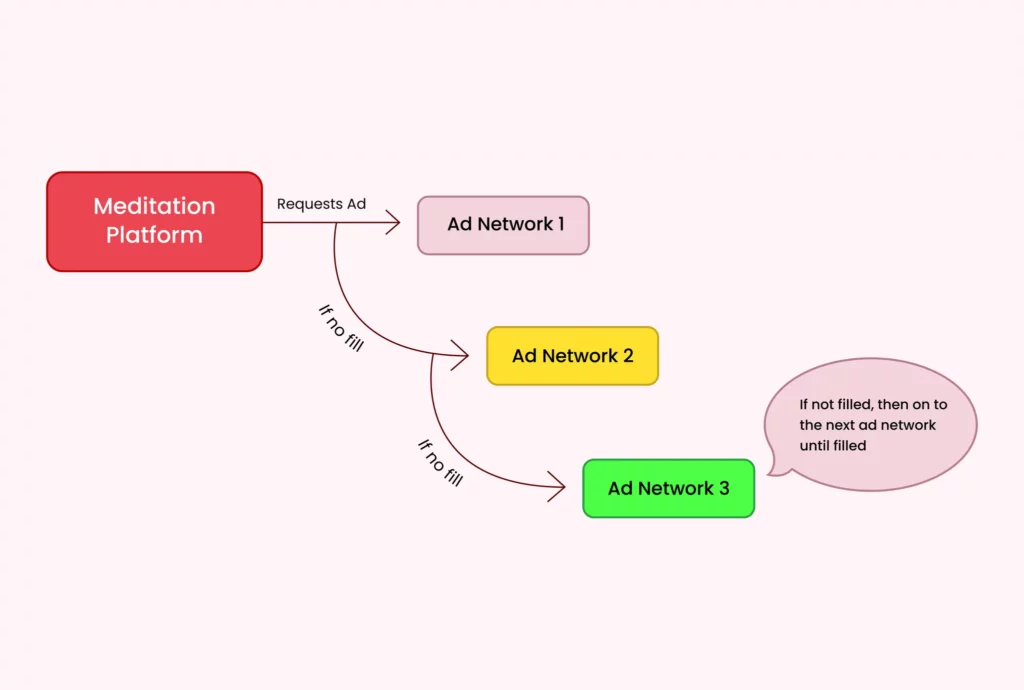
How does Ad Mediation benefit Publishers?
Ad mediation network benefits publishers in many ways, and some of them are listed here:
Easy Integration and Management
Ad mediation platforms simplify the integration process by allowing publishers to manage multiple ad networks through a single SDK. This reduces the technical complexity and time required for setup, enabling publishers to focus more on their core business activities.
Access to Multiple Ad Networks
Ad mediation provides access to a variety of ad networks, ensuring a steady stream of advertisements. This diversity helps publishers achieve higher fill rates that enhances the ad revenue potential for publishers.
Simplified Reporting
Ad mediation simplifies reporting by consolidating all the ad networks data at one place. This streamlined reporting makes it easier to analyze performance metrics, track revenue, and make informed decisions to optimize ad strategies effectively.
Improved Fill Rates and eCPM
Ad mediation improves fill rates and effective cost per mille (eCPM) by dynamically selecting the best-performing ads from multiple networks. Without ad mediation, it’s impossible to drive an ad. This maximizes revenue by ensuring that the highest-paying ads are served to users.
Challenges and Limitations of Ad Mediation
Ad mediation surely helps developers to optimize ad revenue by managing multiple ad networks but does have challenges and limitations listed below:
Use of Waterfall Auction Method
The first limitation of ad mediation is the use of the waterfall method. Unlike header bidding, impressions are offered to multiple ad networks one-by-one. Here, the ad network matching or offering more than the floor price wins the impression. Due to this method, publishers can lose out on untapped revenue which they could have got using header bidding.
Lack of Revenue Transparency
Publishers often face issues with the insights offered by ad mediation platforms, as the insights are not as granular as the ones in header bidding platforms. Due to this lack of revenue transparency, developers have to face various complications when optimizing their ad strategies.
Integration Complexity
Integrating multiple SDKs from different ad networks is the biggest challenge when working with ad mediation. Moreover, each additional SDK increases the app’s size, which can negatively impact download rates, especially in regions with limited data access.
The Risk of Low-quality Ads Being Served
There can be several issues related to quality control, as bidders are often served with lower-quality ads. This negatively affects the user experience and increases the bounce rate. The only solution is to monitor ads and try to maintain a strict quality, but this task is itself a challenging one.
Header Bidding vs Ad Mediation: What are the Differences?
Header bidding and Ad mediation share some similarities, but they differ significantly in multiple aspects. Header bidding allows publishers to offer their ad inventory to multiple ad exchanges at once, while ad mediation consolidates multiple ad networks into a single ad server.
Ad Selling Approach
As mentioned, header bidding allows publishers to offer their ad inventory to multiple ad exchanges. It works by publishers inserting a header tag on their website’s header, a piece of code that sends bid requests to multiple ad exchanges. After that, advertisers start bidding for publishers’ ad space in real-time, and the one with the highest bid wins.
Talking about ad mediation, publishers manage and optimize their ad inventory by selecting the best ad networks to serve an ad for each impression. Unlike header bidding, to get started with this, publishers need to integrate multiple ad networks into a single ad server, which selects the best-performing network for each ad impression based on predefined rules.
Revenue Potential
Next, implementing header bidding can result in higher revenue potential for publishers. It’s because ad inventory is sold to the highest bidder in the auction. Apparently, this also leads to increased competition and higher CPM (Cost Per Mile), which translates to high revenue.
Now coming to ad mediation, while it still helps publishers optimize their ad inventory, it may not result in maximum revenue potential. When you rely on the ad server, it selects the best-performing network based on predefined rules, which may not necessarily result in the highest bid.
Implementation Complexity
Header bidding can be more complex to implement compared to ad mediation. Publishers need to insert a header tag on their website’s header, which involves multiple ad exchanges and bidders. This can require more technical knowledge and resources.
Ad mediation, on the other hand, is simpler to implement as it involves integrating multiple ad networks into a single ad server. Publishers can set up rules and preferences for each network, and the ad server handles the rest.
Optimization Capabilities
Header bidding can help publishers optimize their ad inventory by exposing them to multiple ad exchanges and bidders. This can lead to increased competition and higher CPMs. However, optimization capabilities may be limited to the bidders and ad exchanges used in the header bidding setup.
On the other hand, Ad mediation allows publishers to optimize their ad inventory by selecting the best-performing network for each impression. This can help maximize revenue by choosing the network most likely to fill the impression at the highest CPM. The ad server can also fill unsold inventory with ads from other networks, ensuring maximum revenue.
Latency and Page Load Times
Latency and page load times can be two major decisive factors that help you differentiate between header bidding and ad mediation. When it comes to header bidding, it generally reduces latency because the bidding process takes place on the server, which results in quick page load time and better UX. On the other hand, ad mediation increases latency and slows down the page load times.
The reason behind that is ad mediation involves several sequential ad requests made on the client side, and each ad network is addressed one after the other to fill the ad space.
From what we have learned so far, both ad mediation and header bidding can be effective options for increasing ad revenue. However, choosing between both concerns the publishers’ needs and goals.
Key Takeaways – Header Bidding vs Ad Mediation
1. Header bidding involves offering ad inventory to multiple ad exchanges simultaneously, allowing bidders to compete in real-time. Whereas, ad mediation involves integrating multiple ad networks into a single ad server, which selects the best-performing network based on predefined rules.
2. Next, header bidding can result in higher revenue potential for publishers as inventory is sold to the highest bidder, while ad mediation helps publishers optimize ad inventory by prioritizing the top-performing networks’ bids based on previous bidding data.
3. Implementation of header bidding can be more complex than ad mediation, as it involves inserting a header tag on the website’s header and requires technical knowledge and resources.
4. Ad mediation is easier to implement than header bidding, as it involves integrating multiple ad networks into a single ad server and setting up rules and preferences for each network.
If all of this sounds too perplexing, look no further than AdPushup.
Why Should You Rely on Adpushup?
Merely deploying header bidding or ad mediation in your ad stack isn’t enough. Consistently optimizing it with technical improvements is the need of the hour.
This is what AdPushup’s header bidding and Ad Mediation solution does. Through our multiple optimization features using data science and machine learning, we help publishers maximize their yield.
With our header bidding solution, you get:
- Automatic demand partner selection according to optimum requirements
- Smart timeout management
- Freedom to bring your own demand
- Bid monitoring and discrepancy resolution
FAQs – Header Bidding vs Ad Mediation
Header bidding allows all demand sources to compete for ad inventory at the same time, whereas ad mediation selects the best ad network for each ad request. Header bidding is typically used for programmatic advertising, while ad mediation is often used for traditional ad networks.
No, they are not mutually exclusive. Some publishers may use both header bidding and ad mediation to maximize their ad revenue.

Deepak has a keen eye for detail and a deep understanding of the ad tech landscape. Whether it’s through in-depth articles, thought-provoking insights, or compelling storytelling, he’s dedicated to helping people navigate the complex world of ad tech with the simplicity of his words.